Keynotes Speakers
Keynotes
14th International Conference on Intelligent Environments (IE'18) 25-28 of June 2018, Rome - Italy http://www.intenv.org/
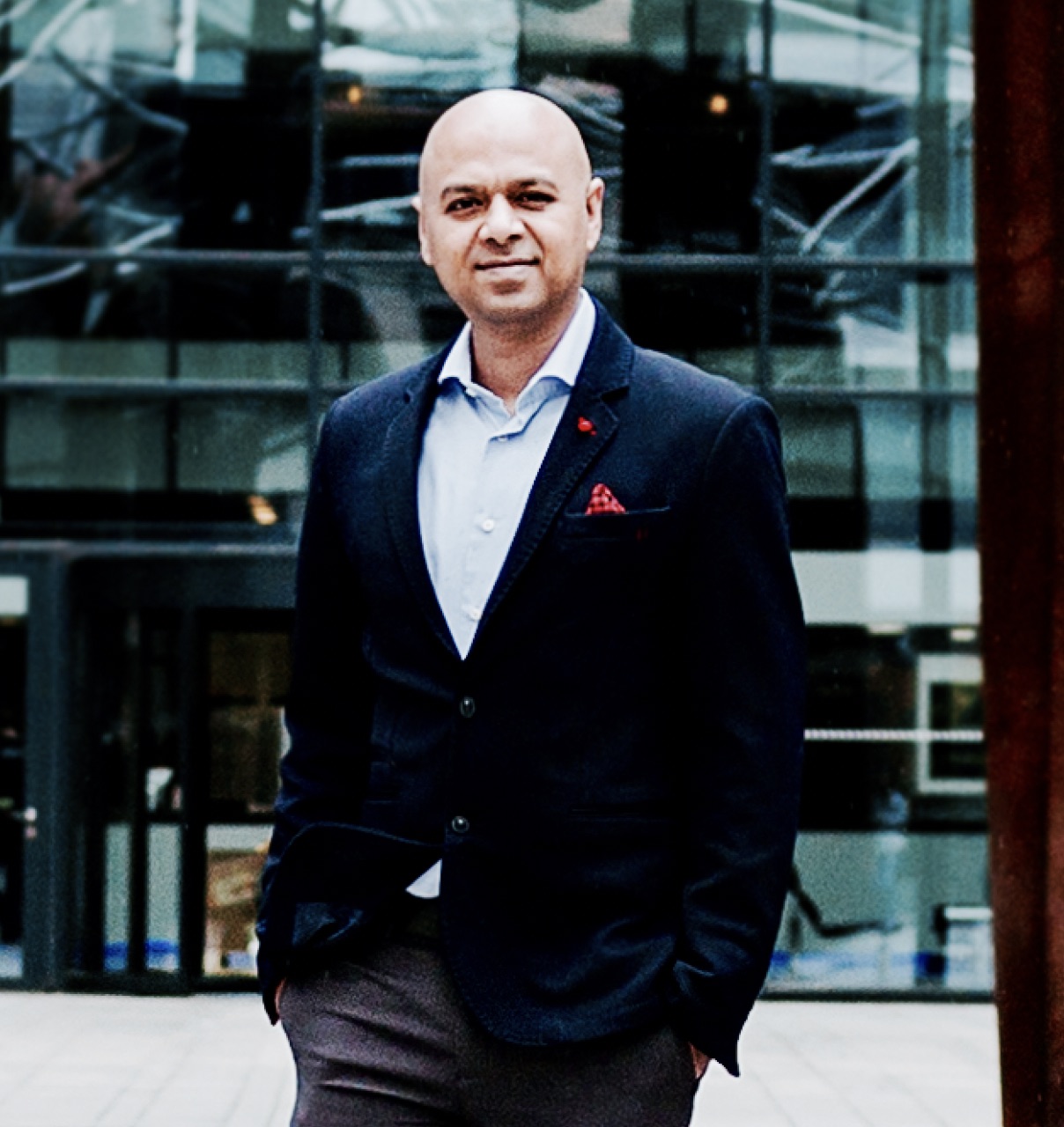

Computational Behavior Modelling for the Internet of Things
The Internet of Things is upon us, and we are observing a monumental effort from the industry and academia to make everything connected. Naturally, to understand the needs of these connected things, we need a better understanding of humans and where, when, and how they interact. This behavioural understanding would help us to create digital services and capabilities that fundamentally change the way we experience our lives. In this talk, I will explore the system and algorithmic challenges in modelling human behaviour. I will discuss how mobile and wearable devices together with the wireless network can be used as a multi-sensory computational platform to learn and infer human behaviour and to design user-centred connected services across Smart Built Environment and Quantified Lifestyle.
Dr Fahim Kawsar leads the Internet of Things research at Bell Labs, Cambridge, UK and holds a Design United Professorship at TU Delft, Netherlands. His current research explores novel algorithms and system design techniques to build transformative multi-sensory systems for disruptive mobile, wearable and IoT services. He borrows tenets from Social Psychology, learns from Behavioural Economics and applies Computer Science methods to drive his research. He is a frequent keynote, panel and tutorial speaker, hold 15+ patents, organised and chaired numerous conferences, (co-)authored 100+ publications and had projects commissioned. He is a former Microsoft Research Fellow and has worked before at Nokia Research, and Lancaster University. His work can be viewed at http://www.fahim-kawsar.net .

Visible Light Communications and Sensing with COTS Techniques: A Path to Efficient Smartness
Given the fast developments in science and technology, we are demanding more and more intelligence from our ambient environments. As information serves as a basic building block for creating intelligence, an intelligent environment depends heavily on the ability of gathering and communicating information, which in turn relies on its sensing and networking infrastructure. Nonetheless, deploying such an infrastructure using existing technologies can be highly inefficient. For example, existing smart building/home projects require a huge number sensors even in a small room and many WiFi/Bluetooth access points for the purpose of intelligence, which is neither effective nor efficient: on one hand, this large scale infrastructure becomes another complicated system that requires further managing and coordination, and on the other hand, the infrastructure itself incurs non-negligible energy consumption that adds on to the already high carbon footprint of modern buildings.
To this end, our propose a supplementary intelligence framework that basically piggybacks on the infrastructure already existing in a building, so that both effectiveness and efficiency can be retained in the process of enhancing the intelligence of our ambient environments. Essentially, our proposal leverages the pervasively available lighting infrastructure for indoor spaces. First of all, an indoor lighting infrastructure produces visible light that exists everywhere within a building. Secondly, the trend of applying Light-Emitting Diode (LED) based lighting infrastructure is becoming increasingly prominent. Last but more importantly, LED luminaires can be digitally controlled to offer far more functions than illumination itself. We have been working on this LED-enabled Efficient Smartness project for a couple of years, and I intend to summarize our progress into the following two aspects:
- Visible Light Communication (VLC): Although it has been a research topic for many years, its theories are still far from practice. Our intention is to study and build a practical VLC platform that offers sufficient bitrate so as to partially replace Wi-Fi, using only Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) devices.
- Visible Light Sensing (VLS): While VLS enabled gesture recognition has been proposed very recently, we are aiming at a much larger scale application. In particular, we report our last results on detecting human occupancy indoors through VLS, as well as our novel idea of “light sensing light”, i.e., using the lighting infrastructure to act as sensors, while utilizing the visible light produced by the infrastructure to serve as the media.
Dr. Jun Luo received his BS and MS degrees of Electrical Engineering from Tsinghua University, Beijing, China in 1997 and 2000, respectively. He obtained his PhD degree of Computer Science from EPFL (Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne) in 2006. His PhD dissertation was done under the supervision of Prof. Jean-Pierre Hubaux in the Laboratory for Computer Communications and Applications (LCA) . He later worked as a post-doctoral research fellow in Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at University of Waterloo for two years (2006-2008), under the supervision of Prof. Catherine Rosenberg. He joined NTU-SCSE as an Assistant Professor in 2008, and he was promoted to Associate Professor in 2014. He served as the Deputy Director of Centre for Multimedia and Network Technology from 2010 to 2013.
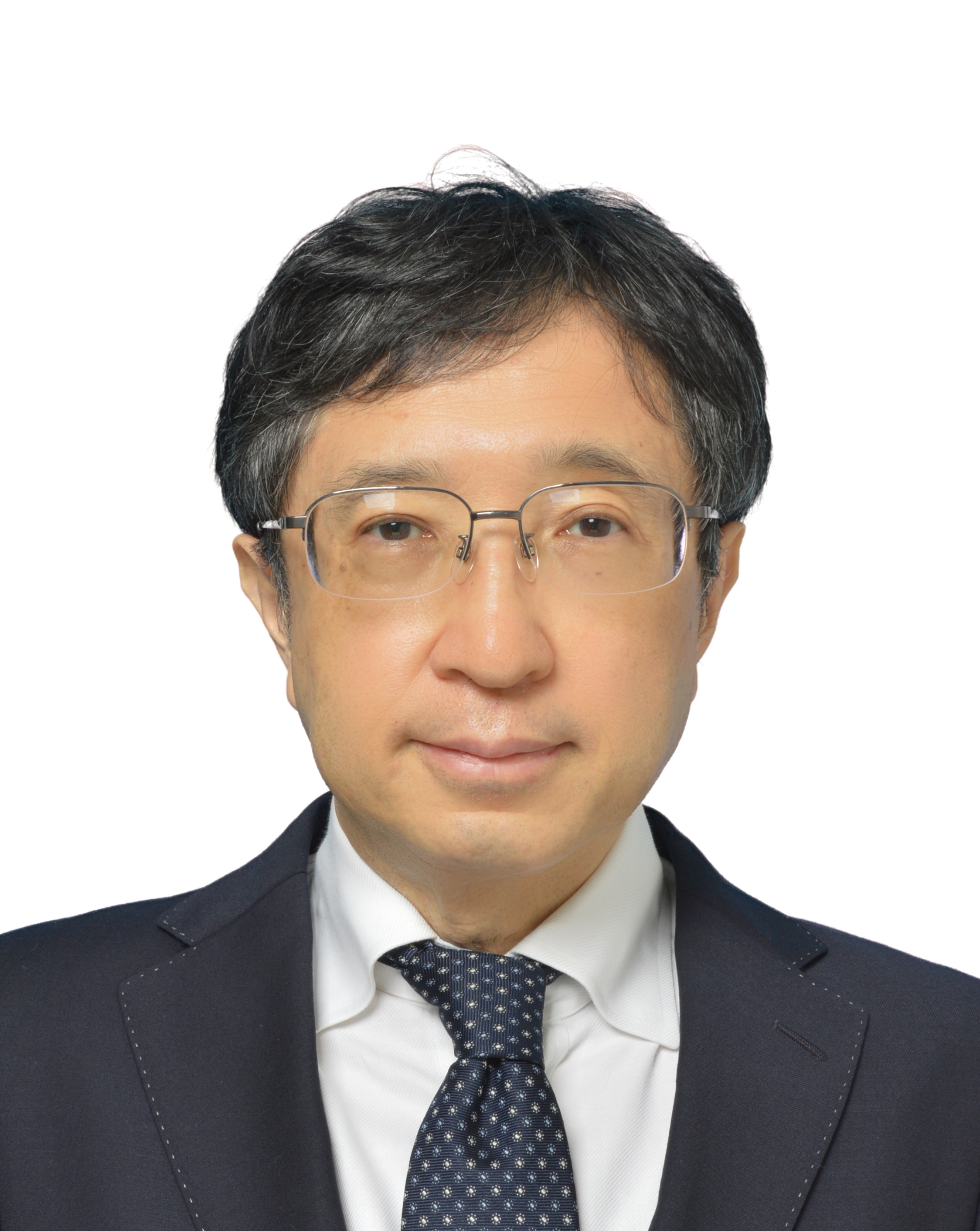

Intelligent Interactive Space - Fusion of ICT, ET and Robot Technology
Intelligent Interactive Space is the space which is observed by sensors and interacts with Human through mechatronics/robotics equipment. Current emerging advancement of IoT and Cyber Physical System encourages to realize the Intelligent Interactive Space in our daily life. Human behaviors and physiological states are acquired anytime anywhere by networking of external sensors and wearable sensors in the notable space such as an inside of a car, a room, a hospital room, a school room, an office, and etc. Then a huge amount of information are analyzed and learned by machine so that the space can assist Human by using mechatronics/robotics equipment. In my presentation, firstly I will define the Intelligent Interactive Space from a view point of creating values to Human daily life. Then I will show our physiological measurement sensors to keep our health, and as for mechatronics/robotics equipment I will explain our very small direct drive servo actuators. Finally as an on-going research I will discuss a walking battery robot to maintain energy power supply in the Intelligent Interactive Space.
Hideki HASHIMOTO(IEEE Fellow, SICE Fellow, RSJ Fellow) received the B.S., M.S. and Dr. of Engineering from the Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Tokyo in 1981, 1984 and 1987 respectively.
He joined the Institute of Industrial Science of the University of Tokyo as a lecturer in April of 1987.He was an associate professor from July of 1990 to March of 2011. He has been a professor at Dept. of Electrical, Electronics and Communication Engineering, Chuo University, Tokyo, Japan since April of 2011.
He was a visiting scientist at LIDS (Laboratory for Information and Decision System) and LEES(Laboratory for Electromagnetic and Electronic Systems) of MIT from September of 1989 to August of 1990. He was an Invited Distinguished Professor at Seoul National University from 2009 to 2012, and he has been a visiting professor at Budapest University of Technology and Economics since 2014.
He was the founding general chairman of 1997 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM). And he was a program chairman of IEEE/RSJ IROS in 2000.
His research topics are Intelligent Space, Intelligent Systems, Robotics, Control. And Energy Management.